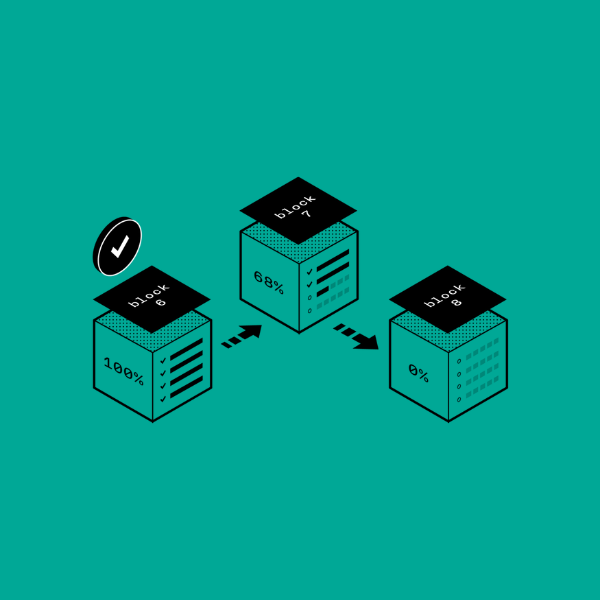
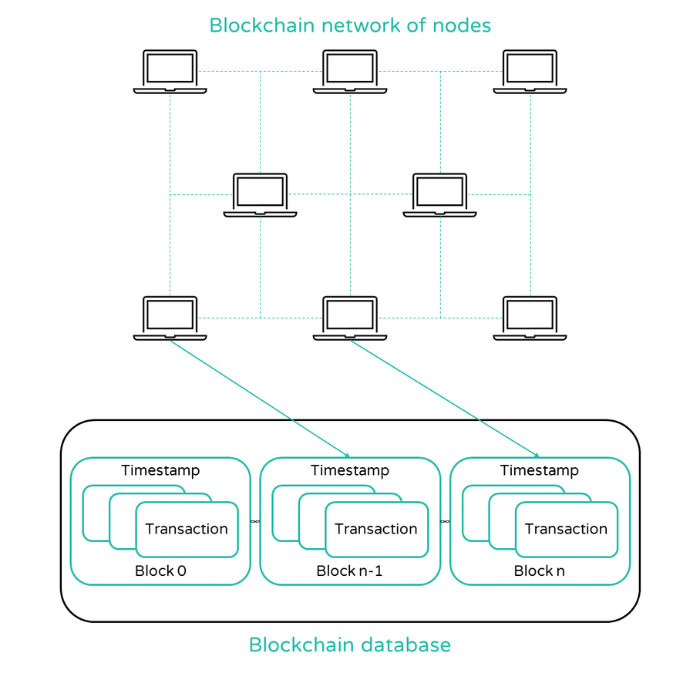
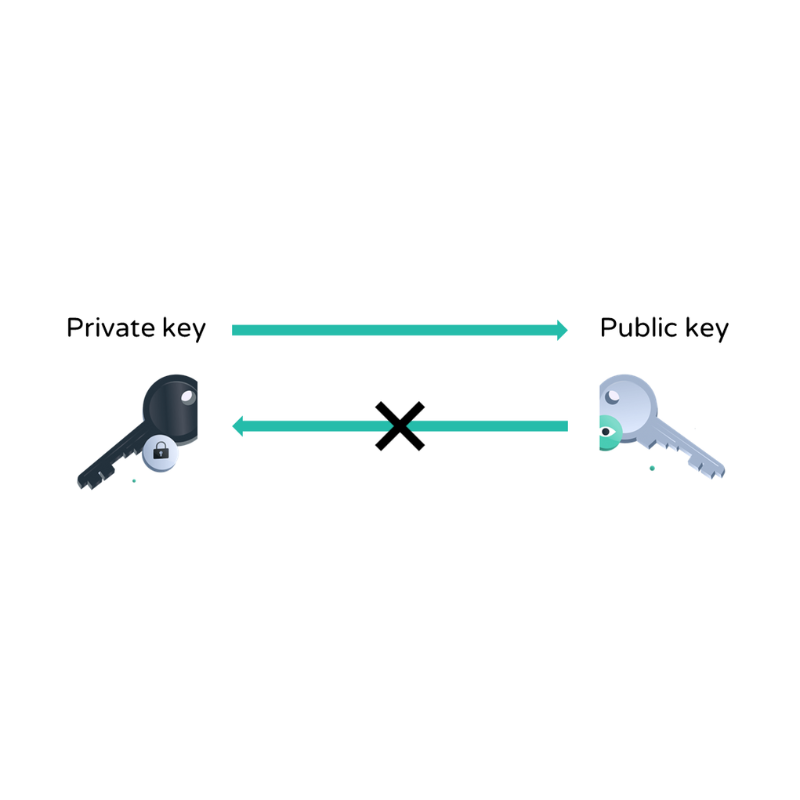
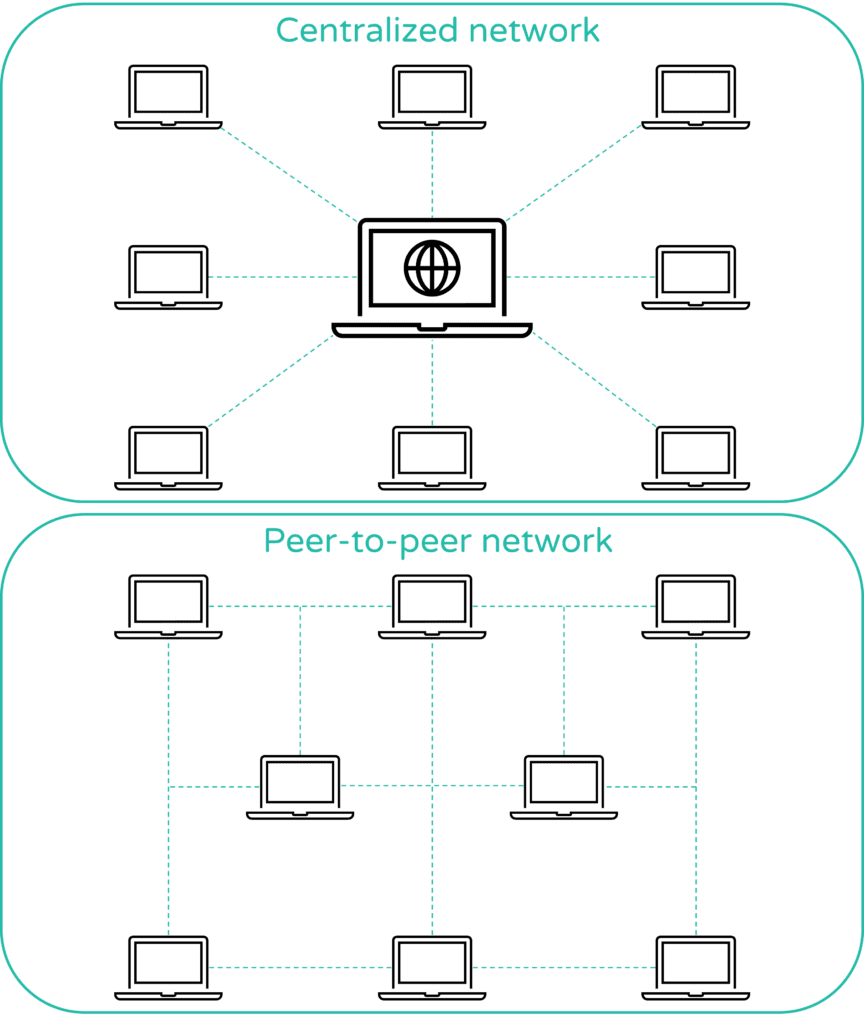
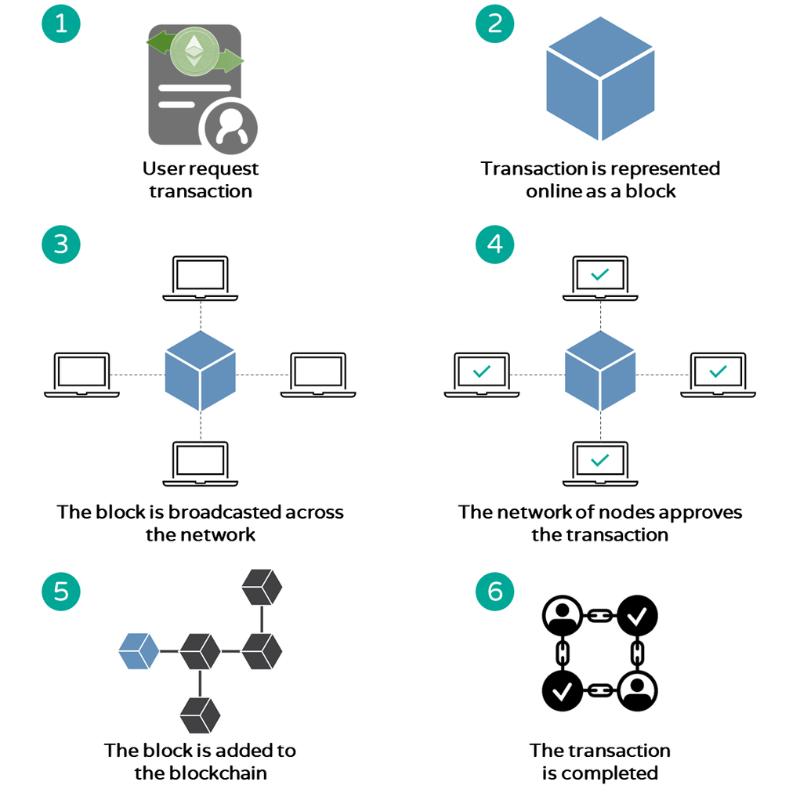
What are blockchains?
Blockchains form the infrastructure NFTs, cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications exist on top of. As blockchains are controlled by code and are decentralized, NFTs and cryptocurrencies are available worldwide, 24/7. Here we explain the basics of blockchain.